BLOGS
GDP contraction decoded
Although most people expect India’s GDP to experience a substantial contraction when the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI) released first quarter data on Monday (April, May , June) of the current fiscal year, the general consensus was that the decrease would not exceed 20%.
Table of Contents
Toggle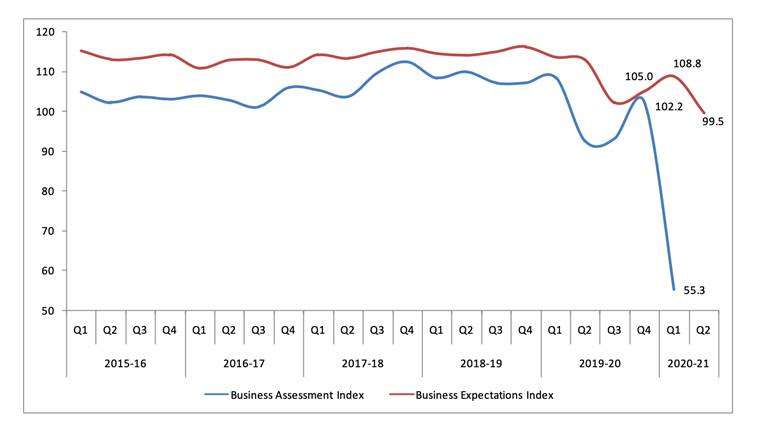
It turns out that GDP contracted 24% percent in the first quarter. In other words, the total value of goods and services produced in India in April, May and June of this year is 24% lower than the total value of goods and services produced in India in the same three months of the year last year.
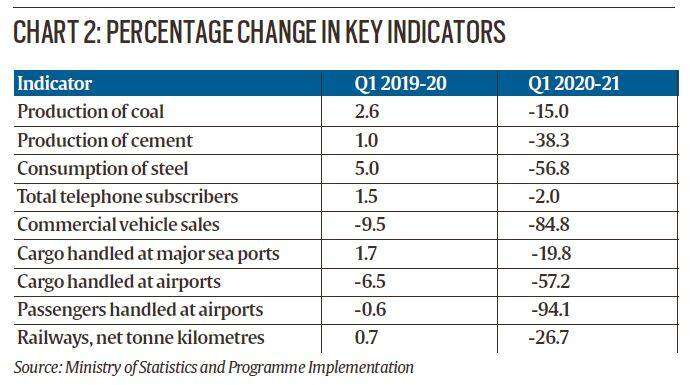
Almost all of the main economic growth indicators, be it cement production or steel consumption, show a sharp contraction. Even the total number of telephone subscribers contracted this quarter. What’s worse is that due to widespread crashes, the data quality is suboptimal and most observers expect this number to worsen when revised in a timely manner.
What is the biggest implication?
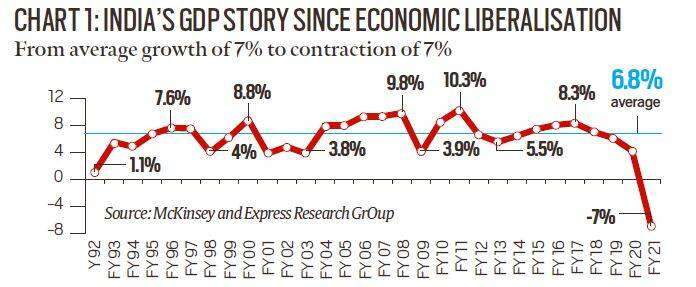
With GDP contracting more than expected by most observers, it is now believed that full annual GDP could deteriorate as well. A fairly conservative estimate would be a contraction of 7% for the full year. Figure 1 puts this in perspective. Since economic liberalization in the early 1990s, the Indian economy has recorded an average GDP growth of 7% each year. This year it is likely to turn into a turtle and decrease by 7%.
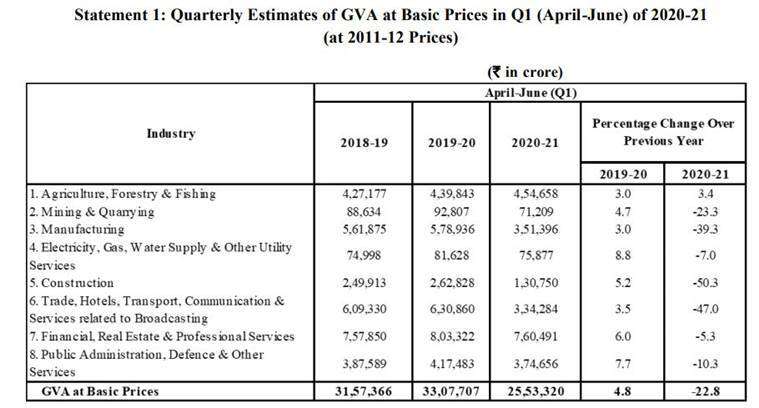
In terms of gross value added (an indicator of production and income) by different sectors of the economy, the data shows that, with the exception of agriculture, where GVA increased by 3.4%, all other sectors of the economy have seen your income drop.
The most affected were construction (–50%), trade, hotels and other services (–47%), manufacturing (–39%) and mining (–23%). It is important to note that these are the sectors that generate the most new jobs in the country. In a scenario where each of these sectors contracts so sharply, i.e. their production and incomes decline, more and more people would lose their jobs (decrease in employment) or not get them. (unemployment increase ).
What are the causes of the contraction in GDP?
Why was the government unable to stop it?
- In any economy, the total demand for goods and services, that is, GDP, is generated by one of the four growth engines.
- The most important driver is demand from consumers like you. Let’s call it C, and in the Indian economy it was 56.4% of all GDP before this quarter.
- The second most important driver is the demand generated by private sector companies. Let’s call it me, and it was 32% of all India’s GDP.
- The third driver is the demand for goods and services generated by the government. Let’s call it G, and it was 11% of India’s GDP.
- The final driver is net demand for GDP after subtracting imports from India’s exports. Let’s call it NX. In the case of India, it is the smallest engine and, since India generally imports more than it exports, its effect is negative on GDP.
Then total GDP = C + I + G + NX
Now look at Chart 4. It shows what happened to each of the engines in the first quarter.
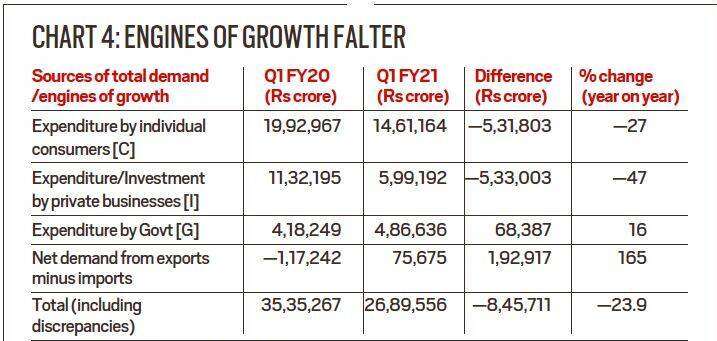
- Private consumption, the biggest driver of the Indian economy, fell 27%. In monetary terms, the decrease is 5.31.803 crore compared to the same quarter last year.
- The second driver, business investment, fell further: it is half of what it was in the same quarter last year. In monetary terms, the contraction is 5.33,003 million rupees.
- So the two biggest drivers, which accounted for over 88% of India’s total GDP, experienced a massive contraction in the first quarter.
- NX or net export demand turned positive in this first quarter as India’s imports fell more than its exports. If, on paper, this boosts overall GDP, it also indicates an economy where economic activity has collapsed.
- This brings us to the ultimate engine of growth; government. As the data shows, government spending increased by 16%, but this was not close enough to compensate for the loss of demand (energy) in other sectors (engines) of the economy.
Examining the absolute numbers provides a clearer picture. When the demand for C and I fell by Rs 10.64,803 crore, government spending increased only by Rs 68,387 crore. In other words, public spending increased, but it was so low that it could only cover 6% of the total decrease in demand from individuals and companies. The net result is that, although, on paper, the share of public spending in GDP has increased from 11% to 18%, the reality is that total GDP has fallen by 24%. It is the lowest level of absolute GDP that makes the government seem like a bigger growth engine than it is.
What is the exit?
When income falls dramatically, individuals reduce their consumption. When private consumption falls sharply, companies stop investing. Since these two decisions are voluntary, there is no way to force people to spend more and / or force companies to invest more in the current scenario. The same logic also applies to exports and imports.
In these circumstances, there is only one engine that can drive GDP and that is the government (G). Only when the government spends more, either by building roads and bridges and paying salaries, or by distributing money directly, can the economy recover in the short and medium term. If the government does not spend enough, the economy will take time to recover.
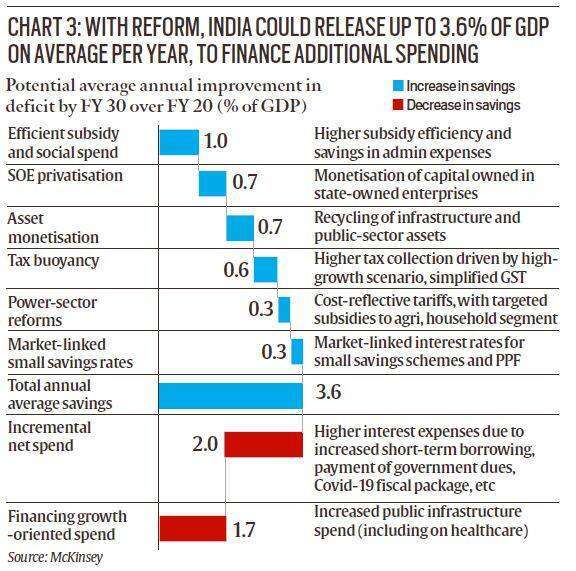
What prevents the government from spending more?
Even before the Covid crisis, public finances were overburdened. In other words, it wasn’t just about borrowing, but about borrowing more than you should have. As a result, you don’t have that much money today.
You will have to think of innovative solutions to generate resources. Chart 4 from the McKinsey Global Institute provides ways in which the government can increase an additional 3.5% of GDP.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
FY 2019-20 GDP growth rate 4.2%
The Indian economy grew at a rate of 3.1% in the fourth quarter of the last fiscal year, with the publication of Q4 GDP growth rate data MOSPI, the entire period growth rate of 2019-2020 pegged at 4.2%. The government also reduced GDP growth in the first, second, and third quarters to 5.2%, 4.4%, and 4.1%, respectively. GDP growth in the fourth quarter becomes significant as it includes the one-week lockdown numbers.
Table of Contents
ToggleReal GDP or Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at constant prices in the year 2019-20 is now estimated to attain a level of Rs 145.66 lakh crore, as against the first revised estimate of FY19 GDP of Rs 139.81 lakh crore. GDP at constant prices in Q4 of 2019-20 is estimated at Rs 38.04 lakh crore, compared to Rs 36.90 lakh crore in Q4 of 2018-19.
The government has also revised down the GDP growth in Q1, Q2, and Q3 to 5.2 per cent, 4.4 per cent, and 4.1 per cent respectively., July-Sep GDP growth revised to 4.4% from 5.1% earlier and Oct-Dec GDP growth revised to 4.1% from 4.7% earlier.
Q4 growth highlights
- Manufacturing sector growth at -1.4% vs 2.1% on year.
- Mining sector growth at 5.2% against -4.8% on year.
- Farm sector growth is at 5.9% against 1.6% on year.
- Jan-March GVA has expanded 3% on year.
- Govt sees FY20 GDP growth at 4.2% on-year.
Meanwhile, the growth rate of eight core industries for April 2020 fell by 38.1 per cent, compared to a fall of 9 per cent in March 2020.
- The output of electricity fell by 22.8 per cent,
- output of cement fell by 86 per cent;
- steel by 84 per cent;
- fertilizer by 4.5;
- refinery by 24.2 per cent;
- crude oil by 6.4 per cent; and
- Coal by 15.5 per cent in April 2020.
Even before the appearance of coronavirus cases in India, the country’s economy was struggling for a prolonged economic slowdown. A significant drop in economic activity due to the national lockdown led by the coronavirus in the first quarter of the current tax could cause the quarterly GDP to fall.
According to the SBI Ecowrap report the contraction of GDP in the first quarter of FY21 can reach 40%, indicating the possibility of a smart recovery of second-quarter GDP of up to 7.1%, thanks to the country’s capacity to support demand, OSE chief economist Soumya Kanti Ghosh said that the loss of GDP in the first quarter of fiscal 2011 will be huge and could even exceed 40%.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
AatmNirbhar Bharat AIBE AIBE17 CACP CBSE CLAT CLAT 2025 CORONA VACCINE Coronavirus COVID 19 COVID19 CUET PG CUET UG CUET UG 2023 DU Admission Facebook Fiscal deficit fiscal stimulus FOREIGN EXCHANGE RESERVES GDP GI Tag GI TAGS In iNDIA GST GST COMPENSATION indian economy INDO-CHINA BORDER DISPUTE INDO-CHINA CONFLICT INFLATION INSTAGRAM JIO lockdown MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE MPC MSP NIRF nobel prize 2020 PMI RAFALE FIGHTER JET RBI RBI GOVERNOR RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED REPO Rate RIL twitter UNIVERSITY OF DELHI
Full list of National Sports Award 2020 winners
In the first virtual national sports awards ceremony forced due to the coronavirus pandemic, a record 74 Indian sports heroes were honored on the anniversary of the birth of the legend of the hockey, Major Dhyan Chand, which takes place annually. like sports day in India.
Table of Contents
Toggle- All five Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Laureates and 27 Arjuna Laureates, except a few, have registered in various cities to be honored by President Ram Nath Kovind. 60 out of 74 attended the virtual ceremony held at 11 Sports Authority of India (SAI) centers in various cities.
- While the winners of Khel Ratna, Rani Rampal (hockey), Manika Batra (TT), Mariyappan Thangavelu (Athletics) attended the ceremony, Rohit Sharma (Cricket) were lost due to IPL commitments 2020 and Vinesh Phogat (Wrestling)tested positive for the coronavirus respectively. As Manika connected from Pune, Mariyappan and Rani joined the SAI center in Bengaluru.
- Along with Rohit and Vinesh, winners Arjuna Ishant Sharma (Cricket) and Satwiksairaj Rankireddy (Badminton) also missed the ceremony after the latter tested positive. Ishant is also in the United Arab Emirates for the upcoming IPL season.
- President Kovind applauded as the names of the award-winning attendees were spoken and their accomplishments cited, as was the convention. “This is the first COVID-era awards ceremony that the president has attended,” Sports Minister Kiren Rijiju said at the start of the ceremony.
- The prize money for the Khel Ratna has been increased to Rs 25 lakh from the previous amount of Rs 7.5 lakh. The Arjuna laureates, 22 of whom attended the ceremony, received Rs 15 lakh, which is Rs 10 lakh more than the above sum.
- Dhronacharya (lifetime) laureates, who had previously received Rs 5 lakh, received Rs 15 lakh, while regular Dhronacharya came with Rs 10 lakh instead of Rs 5 lakh per scholar.
- Dhyanchand fellows received Rs 10 lakh instead of Rs 5 lakh. Former Indian athletics coach Purushotham Rai, 79, died of a heart attack on Friday, hours before receiving the Dronacharya Award, the most important athletic award for a coach in India.
- Purushottam Rai’s name was announced for this year’s Dronacharya Awards and he was scheduled to participate in Bengaluru’s Virtual Congratulations Program. He was even present at the rehearsals of the congratulatory ceremony for Vikasa Soudha scheduled for Saturday, National Sports Day.
Full list of National Sports Award winners
- Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award: Rohit Sharma (Cricket), Mariyappan Thangavelu (Para Athletics), Manika Batra (Table Tennis), Vinesh Phogat (Wrestling), Rani Rampal (Hockey).
- Arjuna Award: Atanu Das (Archery), Dutee Chand (Athletics), Satwik Sairaj Rankireddy (Badminton), Chirag Chandrasekhar Shetty (Badminton), Vishesh Bhriguvanshi (Basketball), Manish Kaushik (Boxing), Lovlina Borgohain (Boxing), Ishant Sharma (Cricket), Deepti Sharma (Cricket), Sawant Ajay Anant (Equestrian), Sandesh Jhingan (Football), Aditi Ashok (Golf), Akashdeep Singh (Hockey), Deepika (Hockey), Deepak (Kabaddi), Kale Sarika Sudhakar (Kho Kho), Dattu Baban Bhokanal (Rowing), Manu Bhaker (Shooting), Saurabh Chaudhary (Shooting), Madhurika Patkar (Table Tennis), Divij Sharan (Tennis), Shiva Keshavan (Winter Sports), Divya Kakran (Wrestling), Rahul Aware (Wrestling), Suyash Narayan Jadhav (Para Swimming), Sandeep (Para Athletics), Manish Narwal (Para Shooting).
- Dronacharya Award (Life- Time Category): Dharmendra Tiwary (Archery), Purushotham Rai (Athletics), Shiv Singh (Boxing), Romesh Pathania (Hockey), Krishan Kumar Hooda (Kabaddi), Vijay Bhalchandra Munishwar (Para Powerlifting), Naresh Kumar (Tennis), Om Parkash Dahiya (Wrestling).
- Regular Category: Jude Felix (Hockey), Yogesh Malviya (Mallakhamb), Jaspal Rana (Shooting), Kuldeep Kumar Handoo (Wushu), Gaurav Khanna (Para Badminton).
- Dhyan Chand Award: Kuldip Singh Bhullar (Athletics), Jincy Philips (Athletics), Pradeep Shrikrishna Gandhe (Badminton), Trupti Murgunde (Badminton), N Usha(Boxing), Lakha Singh (Boxing), Sukhvinder Singh Sandhu (Football), Ajit Singh (Hockey), Manpreet Singh (Kabaddi), J Ranjith Kumar (Para Athletics), Satyaprakash Tiwari (Para Badminton), Manjeet Singh (Rowing), Late Shri Sachin Nag (Swimming), Nandan Bal (Tennis), Netarpal Hooda (Wrestling).
- Tenzing Norgay National Adventure Awards: Anita Devi (Land Adventure), Col Sarfraz Singh (Land Adventure), Taka Tamut (Land Adventure), Narender Singh (Land Adventure), Keval Hiren Kakka (Land Adventure), Satendra Singh (Water Adventure), Gajanand Yadava (Air Adventure), Late Magan Bissa (Life Time Achievement).
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy: Panjab University, Chandigarh
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Free COVID19 vaccination in India
The free COVID vaccine will be provided to three billion people of frontline and healthcare workers in the first phase of vaccination, Health Minister Harsh Vardhan said on Saturday while providing an update on dry vaccination in the country conducted nationwide in 125 districts at 285 sites.
Table of Contents
Toggle- The minister added that the details of the priority beneficiaries of 27 million million, those over 50 and the minors with comorbidities are also being finalized.
- Speaking of the reluctance to vaccinate, the minister said it was not a new phenomenon. Calling on the Co-WIN digital platform, reconverted from the e-VIN platform to be a true game changer, the minister also explained that this platform will provide real-time information on vaccine stocks , its storage temperature and individualized monitoring of COVID beneficiaries. -19 vaccine.
- He added that this platform will help program managers at all levels through automated assignment of sessions to pre-enrolled recipients, their verification, and generation of a digital certificate after successfully completing the schedule vaccination.
- The first COVID-19 vaccine developed locally in India, Covaxin, has been recommended for “restricted use in emergency situations, subject to multiple regulatory conditions” by the Central Committee of Experts on Subject Standard Medicines (SEC) Control Organization ( CDSCO), here on Saturday.
- The Comptroller General of Medicines (DCGI) will take a final call to approve the deployment of the vaccine in the country. The recommendation was made after a two-day meeting in which the expert group sent Covishield, the vaccine developed by AstraZeneca and the University of Oxford, and manufactured by the Serum Institute of India in Pune. (SII) for approval by DCGI on Friday.
- The Health Ministry, in its statement, said that the SEC has made three recommendations for consideration and final decision by the Comptroller General of Medicines of India (DGCI).
- This includes granting an authorization for restricted emergency use of the vaccine, subject to multiple regulatory conditions in the Serum Institute of India, granting an authorization for restricted use in an emergency situation in the public interest as a precaution abundant, in clinical trial mode, particularly in the context of infection by mutant strains at Bharat Biotech and authorization to conduct phase 3 clinical trials at Cadila Healthcare.
- Meanwhile, the Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) said on Saturday that it had successfully isolated and cultured the British variant of Sars-CoV-2, adding that no other country had so far reported successful isolation and culturing of the variant, according to ICMR.
“Scientists at the ICMR (National Institute of Virology NIV) used Vero cell lines to grow the variant of the virus in the UK,”
said the ICMR.
“UNITED KINGDOM. The virus variant, with all signature changes, is now successfully isolated and cultured from clinical samples collected from returnees in the UK,”
ICMR noted in its tweet.
- India has so far reported 29 cases of the new variant of the coronavirus.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Fourth Press Conference on Economic Reforms
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said in her fourth episode of the economic stimulus package for coronaviruses on Saturday that structural reforms in coal, defense production and aviation will be the target with the aim of boosting growth and create jobs.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Earlier this week, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced a cumulative Rs.20 lakh crore package, almost 10% of GDP, to relieve the various segments of the economy affected by the national lockdown of sets following the coronavirus pandemic.
While this included the March 27 announcement of a Rs.1.7 lakh crore package of free and efficient food grain for the poor for three months and Rs 5.6 lakh crore from the monetary policy of RBI since March. The government in three installments over the past three days has announced a cumulative set of crore Rs 10,73 lakh. The three tranches have provided a variety of steps for small businesses, street vendors, farmers and poor migrants, as well as for shadow banks and electricity distributors, but these are largely systems credit guarantee or new fund creation for banks. and financial institutions. .
Policy reforms to fast-track investment – efforts towards Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Fast track investment clearance through Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS),
- Project Development Cell in each Ministry to prepare investible projects, coordinate with investors and Central/State Governments,
- Ranking of States on Investment Attractiveness to compete for new investments
- Incentive schemes for Promotion of New Champion Sectors will be launched in sectors such as Solar PV manufacturing; advanced cell battery storage; etc
The FM indicated that a program will be implemented in the States through the “challenge mode” for the improvement of the industrial groups of common infrastructure and connectivity. Availability of industrial land / land banks for the promotion of new investments and the provision of information on the industrial information system (IIS) with GIS mapping
- 3376 industrial parks/estates/SEZs in five lakh hectares mapped on IIS
- All industrial parks will be ranked by 2020-21.
FM said there is a need to reduce imports of substitute coal and increase self-sufficiency in coal production. Therefore, the government introduces competition, transparency and private sector participation in the coal sector through an income distribution mechanism instead of a fixed rupee / ton regime. This means that now any party can bid for a block of coal and sell on the open market. For this, the entry rules will be liberalized. The government will immediately offer almost 50 blocks with no eligibility conditions, but only prepayments with a ceiling.
FM said there is a need to reduce imports of substitute coal and increase self-sufficiency in coal production. Therefore, the government introduces competition, transparency and private sector participation in the coal sector through an income distribution mechanism instead of a fixed rupee / ton regime. This means that now any party can bid for a block of coal and sell on the open market. For this, the entry rules will be liberalized. The government will immediately offer almost 50 blocks with no eligibility conditions, but only prepayments with a ceiling.
The sectoral reform of mining will stimulate growth, employment and bring advanced technologies, in particular in exploration. The government is ready to put in place a homogeneous exploration, production and extraction regime. 500 mining blocks will be offered through an open and transparent auction process. The government will also present a joint auction of bauxite blocks and coal ore to improve the competitiveness of the aluminum industry. This will help the industry reduce its electricity costs.
The government will notify a list of weapons / platforms to ban import with annual deadlines and will also guarantee the indigenization of imported spare parts. For this, a separate budget will be provided for the acquisition of national capital. It will also reduce the huge defense import bill. In the defense sector, the government aims to improve the autonomy, accountability and efficiency of artillery suppliers through the Artillery Factory Board. The FDI ceiling for the manufacture of automatic road defense systems will be reduced from 49% to 74%. The government will also begin the acquisition of time-limited defenses and faster decision-making by creating a project management unit (PMU) to support contract management. It will ensure a realistic configuration of the qualitative requirements for general personnel in charge of weapons / platforms and will examine the test and test procedures.
Only about 60% of Indian airspace is available for free. This means that airlines generally offer longer routes. To help streamline this, FM Sitharaman says restrictions on the use of Indian airspace will be relaxed to make civil flight more efficient. This will bring a total profit of Rs 1 crore per year to the aviation sector. It will also reduce fuel consumption and time, which will have a positive environmental impact. The government has announced the auctioning of six other airports under a PPE model. The annual income from this operation in the first round could reach Rs 1 crore / year with an additional deposit of Rs 2.3 trillion for the Airport Authority of India. Additional investments by private actors in 12 airports in the first and second rounds are expected to generate around Rs 13 billion. Six other airports will be released for the third round of auctions. Most defense and civilian aircraft fly abroad for repairs. For this reason, the government has announced the rationalization of the MRO ecosystem to promote repairs and maintenance in the country. The government will launch a pricing policy with reforms, including consumer rights, industry promotion and sector sustainability.
The government says it will boost private sector investments in social-infrastructure projects, like hospitals, by revamping the Viability Gap Funding Scheme. The total outlay for this has been pegged at Rs 8,100 crore.
- The government will enhance the quantum of viability gap funding up to 30 per cent each of total project cost as VGF by Centre and State/Statutory bodies
- For other sectors, VGP existing support of 20% each from GoI and States/Statutuory Bodies shall continue.
- Projects to be proposed by Central Ministries/State governments and statutory entities
The government is boosting private participation in space activities. This will be done by:
- Providing level-playing field for private companies in satellites, launches and space-based services,
- Providing predictable policy and regulatory environment to private players,
- Private sector will be allowed to use ISRO facilities and other relevant assets to improve their capabilities,
- Future projects for planetary exploration, outer space travel etc to be open to private sector,
- Liberal geo-spatial data policy for providing remove-sensing data to tech-entrepreneurs
- Govt to establish a research reactor in PPE basis for production of medical isotopes to promote welfare of humanity through affordable treatment for cancer and other diseases.
- The government will also establish facilities to use irradiation technology for food preservations, again in PPE mode. This technology will compliment agricultural reforms and assist farmers.
- The government will lastly link India’s robust start-up ecosystem to the nuclear sector to foster a synergy between research facilities and tech-entrepreneurs.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Four-year integrated teacher training program to be
Admission will be made by the National Testing Agency (NTA) through the Common National Entrance Test (NCET).

The Ministry of Education (MoE) on Wednesday notified the holistic double specialization diploma offered by BA-BEd, BSc-BEd and BCom-BEd, which is one of the main mandates of the National Education Policy (NEP ) 2020 related to teacher training. It will initially be offered in pilot mode in some fifty selected multidisciplinary establishments across the country.
- The Integrated Teacher Training Program (ITEP) will be available to all students who choose to teach as a profession after high school by choice. The start of the four-year ITEP will be from the 2022-23 academic session.
- National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) has designed the curriculum for this course to enable a student teacher to earn a degree in education as well as a specialized discipline such as history, mathematics, sciences, arts, economy or commerce.
- Admission will be made by the National Testing Agency (NTA) through the National Common Entrance Test (NCET).
- This course will be offered by multidisciplinary institutions and will become the minimum qualification for school teachers.
- ITEP will teach cutting-edge pedagogy and establish a foundation in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), Literacy and Numeracy (FLN), Inclusive Education and an understanding of India and its values / ethics / art / traditions, among others.
Forthcoming MPC meeting
The reorganized Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which will meet this week, is expected to retain the main policy instrument: the repo rate, or the rate at which the RBI lend. funds in banks: unchanged at 4% on Friday, as retail inflation has been above the upper band of the RBI inflation target of 6% for five consecutive months.
Table of Contents
Toggle- After a delay of more than a week, the government appointed Shashanka Bhide, Ashima Goyal and Jayanth R Varma on Monday as independent members of the six-member MPC RBI.
- Bhide is currently Senior Advisor to the National Council for Applied Economic Research, while Goyal is a Professor at the Indira Gandhi Institute for Development Research in Mumbai.
- Varma, who was previously a full-time member of Sebi, is currently a professor at IIM, Ahmedabad. The revamped MPC will meet on October 7, 8 and 9 to finalize monetary policy, the RBI said on Tuesday.
- The central bank was forced to postpone the bi-monthly MPC meeting scheduled for September 29, 30 and October 1, as the government failed to nominate its three members to the six-member panel.
- MPC is the statutory committee that sets the key interest rate and the direction of the country’s monetary policy, as well as the inflation target.
- The terms of the three members appointed by the government in 2016 expired after the previous policy of August 6, when the pension rate remained stable at 4%.
- As Covid-19 deals a devastating blow to the economy and an already weak financial sector, India calls for looser monetary policy.
Uncertainty about growth is essential
- Given the current level of inflation and the uncertainty about the growth outlook, the RBI MPC is expected to take a wait-and-see approach and keep the pension rate at 4%, and continue its accommodative monetary policy at its meeting. ‘October. .
- According to Care Ratings, there would be a status quo on this monetary policy, but given concerns about economic growth, the RBI should maintain the stance of monetary policy at “accommodative”.
- The RBI is likely to guarantee excess liquidity in the banking system mainly through open market operations and special OMOs with the dual objective of improving financial conditions and managing the yield curve.
- Given the current level of inflation and the uncertainty about the growth outlook, the RBI MPC is expected to take a wait-and-see approach and keep the pension rate at 4%, and continue its accommodative monetary policy at its meeting.
- If there is no consensus on the rate or policy at the MPC meeting, there will be a voting process. MPC members have repeatedly differed over the number of buyback rate changes, but ultimately opted for a majority decision.
- Although the MPC cut the policy rate (the repurchase rate) by 250 basis points to 4%, the pass-through of the rate cuts has been rather slow and banks have taken their time passing on profits.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Foreign Universities Indian Campuses

All foreign universities opening their branches in India will be able to conduct courses offline only.
UGC Chairman, Mr. Jagadesh Kumar, today announced the guidelines for foreign universities establishing campuses in India. Kumar has issued guidelines on various topics like Indian Campus Admission Process of Foreign Universities, its Mode of Tuition, Transfer of Funds and more.
All foreign universities wishing to establish their campus in India will only be able to do so after obtaining approval from the University Grants Commission (UGC). “No foreign higher education can establish a campus without UGC’s approval,” the chairman said.
However, foreign universities establishing campuses in the country will get initial approval for a period of 10 years only. The approval granted will be renewed for the ninth year, subject to compliance with certain conditions.
To establish a campus in foreign Indian universities, you will need to be in the top 500 to apply or have a “high reputation” in your respective countries (if the university does not participate in the global ranking). If your rank is between 500 and 100, but the subject rank is higher than the overall, in such cases, institutions may establish their campuses only for ranked subjects. Procedure to come to India
The approval process to set up a campus in India will be done strictly online at first. Interested institutions must apply on the UGC portal with a non-refundable fee and then submit certain documents (as requested by UGC). After receipt of applications, a committee formed by the Commission will review these applications based on the following factors:
- Credibility of the institution
- Programs to be offered by the institution
- Its potential to enhance academic opportunities in India
- Proposed infrastructure
This process will take place within 45 days of the date of the request and the committee will provide its recommendations to the institute. After that, these recommendations will be considered by the Commission and the Commission may decide to grant an approval principle grant and issue a letter of intent to foreign HEIs to establish their campus.
The Commission will grant the institute two years to set up its campus. If an extension is necessary, the Commission will decide on a case-by-case basis. Once the campus is set up, the Commission will check the availability of the campus within 45 days of receiving the availability information from the HEIs.
Offline courses only
- All foreign universities opening their branches in India will be allowed to conduct offline courses only, i.e. foreign universities can only offer full-time programs in physical mode.
- Freedom to choose admissions process, fees, faculty
- Kumar assured that all foreign universities will be free to create their own admission process. However, universities will need to ensure that “the quality of education provided at their Indian campuses is on par with their main campus”.
- In addition to this, foreign HEIs will also have the freedom to design their own fee structure, provided it is transparent and reasonable. The regulations also state that institutes can award partial or full scholarships based on need from their own endowment funds, donations from alumni, etc.
- The Establishment and Operation of Campuses of Foreign Higher Education Institutions in India (UGC) Regulations 2023 also gives foreign institutions complete autonomy to hire faculty and other staff, whether abroad or in India. However, if any faculty members are traveling to India from other countries, they will be required to reside on campus for a considerable amount of time and dedicate resources to Indian campuses.
- “We have also stated in our regulations that campuses established by foreign higher education institutions will ensure that foreign professors appointed to teach on the Indian campus remain on the Indian campus for a reasonable period. It’s not like they come here for a week or two and then come back. They should be here for a reasonable length of time, i.e. at least a semester or two, and then there could be a rotation of these faculty members as decided by these universities,” he said.
- International students also be admitted to these institutes and will be free to enroll Indian and international students at their Indian campuses.
- To ensure there is no chaos in the transfer of funds, Kumar said that all matters related to financing will be in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999. More details on this will be notified by the end of the month.
- Furthermore, UGC reserves the right to inspect these Indian campuses of foreign higher education institutions at any time, and they will not be outside the scope of criminal wrongdoing and other laws.
Read Also:
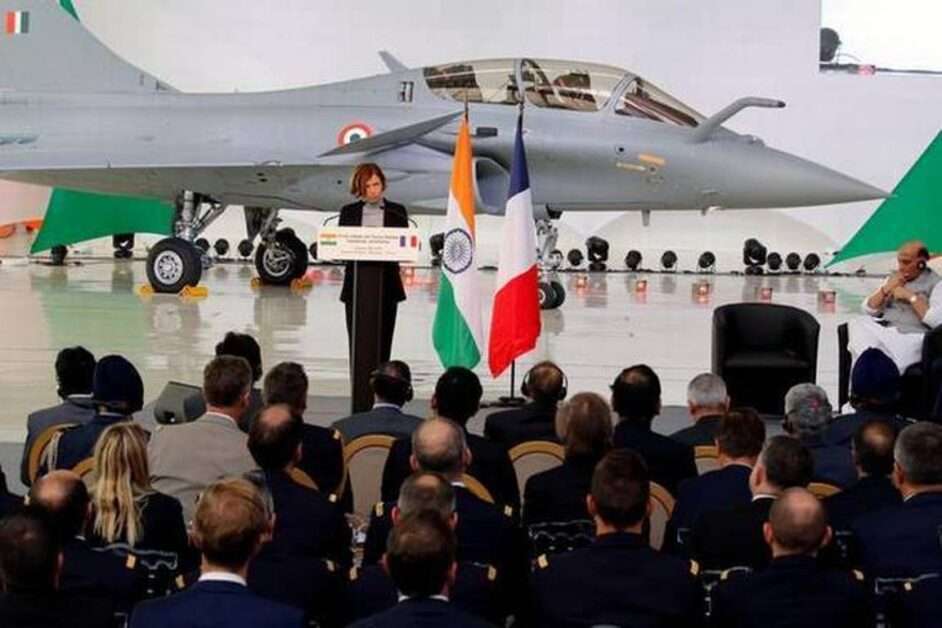
Five Rafale fighter jets were incorporated into the Indian
Five Dassult Rafale planes were incorporated into the Indian Air Force, becoming an operational part of the army. They joined the IAF Golden Arrows squadron based at Ambala Air Base in Haryana. The event was attended by Minister of Defense Rajnath Singh and his French counterpart Florence Parly.
Table of Contents
Toggle- While the planes were delivered to India last October, they did not arrive by air until the end of July, with IAF pilots being trained in France. At the event, Mr. Singh and Air Chief Marshall R.K.S. Bhadauria spoke of border tensions with China, the latter saying the induction could not have taken place at a more opportune time.
- Ms Parly said the planes would give India “an advantage over the whole region”. The role of the jets in maintaining peace in the Indo-Pacific, another point of friction with China, was also mentioned by the ministers of India and France.
- The purchase of the Rafale aircraft had sparked much controversy over the deal with France. Now the plane is joining the military at a time when India faces one of the biggest national security crises. These two factors together give importance to the image that appears on the first page.
- Defense Minister Rajnath Singh on Thursday called the addition of the French Rafale fighter to the Indian Air Force (IAF) “a game changer” and called it a very important step in light of the conditions of security. ruling which “were created along the borders of India”.
- This official ceremony also marks its full operational integration into the IAF, said Air Chief Marshal (ACM) RKS Bhadauria. “They are ready to go and deliver,” he said.
- Five Rafales were part of the No. 17 Golden Arrows squad. It is the first imported fighter to be installed since the arrival of the Sukhoi-30 from Russia in the late 1990s.
- A traditional “Sarva Dharma Puja” took place, followed by an aerial demonstration of the Rafale and the indigenous Tejas aircraft, as well as the Sarang helicopter acrobatic team.
- A traditional water cannon salute was given to the jets prior to their official induction. The five Rafales arrived in Ambala from France at the end of July. They were delivered to India in France last October, but have since been used to train IAF pilots there.
- The aircraft, three single-seater and two two-seater trainers, was flown from France by IAF pilots led by the No. 17 Squadron Commander, Group Captain Harkirat Singh.
- They give the IAF a huge boost in capacity amid the squadron’s decline in strength. At India’s request, France has stepped up deliveries of the Meteor Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile with the first batch of planes. The second batch of four Rafale should arrive in October.
- In September 2016, India signed an Intergovernmental Agreement (IGA) of 7.87 billion euros with France for 36 Rafale in flight condition with 13 India-specific upgrades (ISE).
- The Rafale was initially selected as part of the call for tenders for multi-functional combat aircraft (MMRCA) issued in 2007. But the final deal stalled due to differences and the call was eventually made was withdrawn after Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s announcement of the emergency purchase in April 2015, citing the “critical operational need” of the IAF.
- ISE includes Israeli helmet-mounted displays, radar warning receivers, low-band jammers, infrared search and tracking systems, among others. In addition, the Rafale is armed with the Meteor missile (considered a game changer in the region with a range of over 150 km), the SCALP long-range air-to-surface attack missile and the MICA multi-mission air missile.
- The IAF also arms the Rafale with HAMMER medium-range air-to-surface missiles (Highly Agile Extended Range Modular Ammunition) which are procured on an emergency basis. Ambala Air Base is also home to two Jaguar squadrons fighters and a squad of MiG-21 Bison. Hasimara, in West Bengal, will host the second Rafale squad.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has much to applaud with the arrival of five Rafale multipurpose fighter jets in terms of technology and the increased capabilities it brings.
- In the words of the Air Chief Marshal (ACM) R.K.S. Bhadauria and former ACM B.S. Dhanoa, Rafale is a “game changer”. Summing up what the Rafales bring, ACM Bhadauria said in February that at the time of the Kargil conflict in 1999, India had an advantage over Pakistan in terms of missile capability beyond visual range (BVR).
- According to its manufacturer Dassault Aviation, the Rafale is an omnidirectional fighter capable of assuming the full spectrum of roles: air superiority and air defense, close air support, deep strikes, reconnaissance, anti-ship strikes and nuclear deterrence.
- With its advanced Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar, electronic warfare suite and network-centric capabilities, in addition to its weaponry, the Rafale is now the most advanced fighter in the IAF arsenal, outperforming the SU-30MKI, which must make important updates.
- The Rafale is also the first imported fighter to enter service for more than two decades since the SU-30 in the late 1990s. The Rafale has 14 hard points for weapons and can carry a total external load of more than 9 tons.
- In addition to the Meteor, it is armed with SCALP long-range attack air-to-ground missiles and MICA multi-mission air-to-air missiles. The latest addition, the highly agile modular ammunition medium-range air-to-surface missiles (HAMMER), is purchased through the emergency route.
- Another important factor with the Rafale is that under the contract, at least 75% of the Rafale fleet must be operational, which would make it the most available fighter in the IAF fleet.
- Rafale’s first squad, # 17 Golden Arrows, will be based in Ambala and the second squad will be in Hasimara. All 36 aircraft will be delivered on time by the end of 2021, the Indian Embassy in France announced last week.
- The 7.87 billion euro (59,262 crore) intergovernmental deal, signed in September 2016 between India and France for 36 leaking Rafale aircraft, also includes 13 India-Specific Enhancements (ISE), one-time design and development with a cost of Rs. 9,855 crore. Some of these relate to radar enhancements, helmet-mounted display, the ability to start and operate from high-altitude airfields, advanced infrared search and track sensor, and an electronic very powerful jammer module.
- The deal also incorporates the cumbersome defense procurement process in which government-to-government deals have recently become the solution.
- Rafale was originally selected as part of the tender for medium multipurpose combat aircraft launched in 2007, which in turn was conceived as a replacement project for the Mig-21 in the early 2000s.
- Rafale was selected in 2012, but Negotiations remained blocked due to differences and the bidding was eventually withdrawn after the emergency purchase announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in April 2015, citing “operational need for review” from the IAF.
- However, the 36 Rafale will do little to halt the decline in the IAF’s fighter squad number, which has an authorized strength of 42 squadrons, but is currently down to 31.
- To compensate for this, the IAF is betting on the native Texas Light Fighter (LCA). The 83 LCA-Mk1A contract is in the final phase, adding to the 40 jets already contracted.
- Work is also under way on a more advanced LCA-Mk2. The government recently approved the acquisition of 21 MIG-29 aircraft from Russia, which will add two more squadrons.
- In addition, 12 SU-30MKI aircraft have also been approved, which will replenish the number of Sukhois lost in accidents. The IAF will also eliminate five squadrons of Mig-21s in the coming years.
- As the IAF works to prevent numbers from falling further, the Rafale, which joins the IAF at a time of unprecedented tensions on the border with China, will give the force in the region a qualitative advantage.
- On October 8, 2019, the first Rafale fighter jet of the Indian Air Force (IAF) was delivered to Defense Minister Rajnath Singh in France.
- This step is the latest in a series of necessary but still overdue steps to strengthen the IAF’s combat capabilities.
- The IAF has always been one of the best equipped forces in the region, but it has seen its advantage, particularly quantitative, diminish against China and Pakistan. made in India under the controversial Chapter 7 Defense Procurement (DPP) procedure of 2016.
- It is not known where the budget support will come from for a 114 modern combatant program and, indeed, the capacity of the country to establish and maintain two manufacturers of hunters.
- Defense budgets have been stable for a long time, and as the economy recedes, capital spending is unlikely to increase. Acquisition funding will also necessarily have to compete with research and development funding for upcoming national projects, such as the redesigned LCA Mk.2 and the Fifth Generation Advanced Medium Fighter (AMCA).
- Finally, even if all the short-term acquisitions go according to plan, there is still a period of “acceleration” to manage; the training of air and ground crew, the construction of infrastructure and the commissioning of types. will pose their own challenges that will delay the effective rate of strength building.
- Meanwhile, the Pakistani Air Force (PAF) and the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLAAF) Air Force are not left out. The PAF is responsible for a number of legacy issues that are similar to the IAF.
- However, with the Sino-Pak JF-17 available at low cost and in quantity, as well as access to a wide range of Chinese weapons developed for this type, Pakistan is well placed to recapitalize a significant part of its air force. with relatively modern planes.
- Development and production of the JF-17 can also be expanded to replace PAF’s Mirage fleet on short notice, if required. And as China ramps up its fifth-generation aircraft programs and unit costs drop, there is no doubt that these platforms will also travel to Pakistan.
- The growth of PLAAF is well documented. And in addition to a fourth and fifth generation modernization program, the service benefits from a host of force multipliers, including tankers, surveillance and control aircraft, and long-range bombers.
- Although primarily intended to take on the US military in the Pacific and beyond, China’s formidable air arsenal cannot be ignored in New Delhi.
- As the IAF prepares to welcome its new acquisitions, it must be clear about the challenges it faces at a time when India’s strategic and operational environment is undergoing transformation. Adhocism must give way to strategic thinking if we are to meet these challenges effectively.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Recent Posts
- Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)

- Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026

- CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today

- The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis

- IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile

Categories
Recent Posts
- Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB) 21st December 2024
- Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026 21st December 2024
- CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today 20th December 2024
- The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis 20th December 2024
- IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile 20th December 2024
- AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide 19th December 2024