BLOGS
Kesavananda Bharati passed away
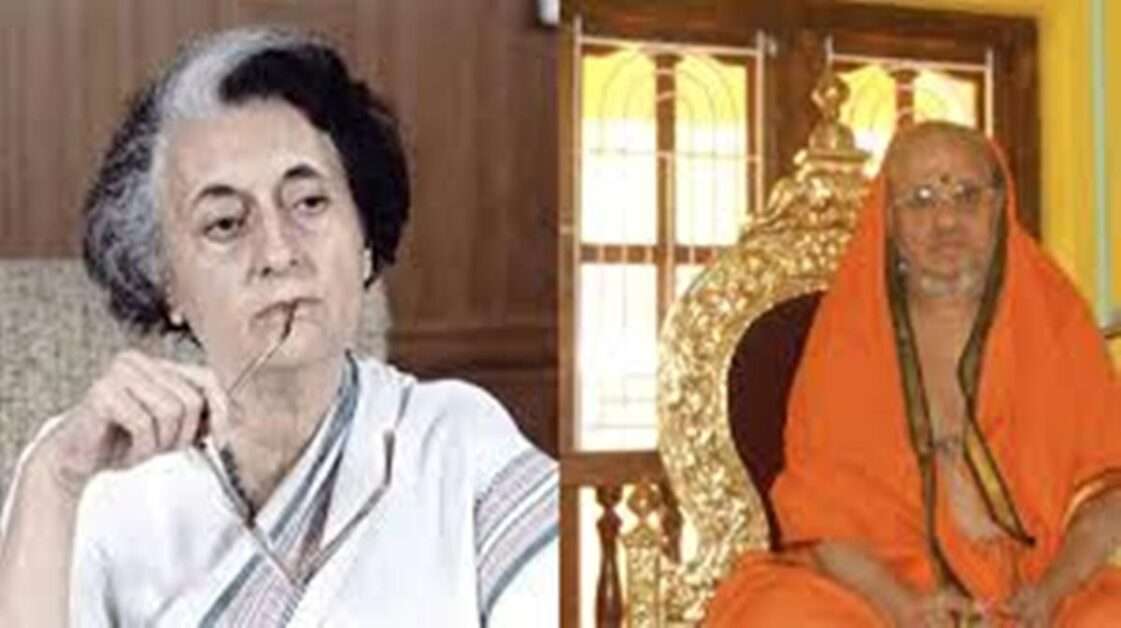
Kesavananda Bharathi, whose legal struggle led to the landmark ruling outlining basic rights under the Constitution, passed away this morning. The head of Edaneer Math in Kasargod, Kerala was 79 years old.
Table of Contents
Toggle- In 1973, Kesavananda filed a lawsuit against attempts by the Kerala government to impose restrictions on the ownership of the stray dog.
- By a narrow majority of 7 to 6, the panel of 13 judges ruled that while Parliament had “extensive” powers, it could not change the basic structure of the Constitution. Since then, the doctrine of basic structure has been regarded as a principle of Indian constitutional law.
- Since then, the doctrine of the “basic structure” has been interpreted to include the supremacy of the Constitution, the rule of law, the independence of the judiciary, the doctrine of the separation of powers, federalism, secularism, the democratic republic, sovereignty, the parliamentary system of government, the principle of free and fair elections, the welfare state, etc. Critics of the doctrine have called it undemocratic, because unelected judges can overrule a constitutional amendment.
- At the same time, his supporters hailed the concept as a safety valve against majoritarianism and authoritarianism.
- The case ranks number one in terms of the longest hearing ever. He was heard by the largest constitutional chamber of 13 judges for 68 days.
- The hearing in the case began on October 31, 1972 and ended on March 23, 1973. In 2018, Kesavananda Bharati received the sentence from Judge VR Krishna Iyer.
- Kesavananda Bharati, the head of the Edaneer Mutt in Kasargod who died Sunday morning, September 6, will be forever remembered for the legal challenge he launched against the government of Kerala, considered by most jurists to be the greatest constitutional case of Indian judicial history.
- By a majority decision of 7-6 rendered in “His Holiness Kesavananda Bharati Sripadagalvaru and Ors. V. In the state of Kerala and Anr ‘, a Supreme Court of 13 judges ruled on April 24, 1973 that the “basic structure” of the Constitution is inviolable and cannot be amended by Parliament.
- Since then, the basic structure doctrine has been regarded as a fundamental principle of Indian constitutional law.
The judges in the Kesavananda Bharati case
The judges of the Constitution bench were divided in two due to serious ideological differences. The majority opinion was delivered by the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India, S M Sikri, and Justices K S Hegde, A K Mukherjea, J M Shelat, A N Grover, P Jaganmohan Reddy and H R Khanna.
What the trial said
- The Court ruled that under Article 368 of the Constitution, which gives Parliament amending powers, something must remain of the original Constitution that the new amendment would not change.
- But although the decision established the basic structure doctrine and ruled that Parliament did not have the power to change it, the court did not define the basic structure itself.
- It only listed a few principles, including federalism, secularism and democracy. The court has since added new features to this concept.
- Today, the “basic structure” is widely interpreted as including the supremacy of the Constitution, the rule of law, the independence of the judiciary, the doctrine of the separation of powers, federalism, secularism, the sovereign democratic republic, the parliamentary system of government, the principle of freedom and fair elections, the welfare state, etc.
The context of the case
- Almost immediately after the adoption of the Constitution, discussions began on the extent of Parliament’s power to amend its main provisions.
- In the early years of independence, the Supreme Court gave Parliament absolute power to amend the Constitution, as evidenced by the verdicts of Shankari Prasad (1951) and Sajjan Singh (1965).
- This is believed to be due to the fact that in those early years the Supreme Court had relied on the wisdom of then political leaders, when prominent figures of the Indian freedom movement were members of parliament.
- In the following years, however, governments amended the Constitution at will to accommodate partisan political interests.
- The Supreme Court in Golaknath (1967) held that the amending power of Parliament could not affect fundamental rights and that this power belonged only to a Constituent Assembly.
- In the early 1970s, the government of then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi enacted major constitutional amendments (24, 25, 26 and 29) to circumvent Supreme Court rulings in RC Cooper (1970), Madhavrao Scindia (1970) and Golaknath (1967).
- In RC Cooper, the court revoked Indira’s bank nationalization policy, and in Madhavrao Scindia, it revoked the elimination of the private portfolios of the rulers of the old princely states.
- The four amendments – 24th (fundamental rights, 1971), 25th (property rights, 1972), 26th (private pockets, 1971), 29th (land reform laws, 1972) – as well as the “IC Golaknath & Ors vs State of Punjab and Anr” (1967), was challenged in Kesavananda Bharati, in which the petitioner sought redress against the Kerala government for two land reform laws.
- Since Golaknath was decided by the 11 judge bench, a larger bench was needed to verify its accuracy, so 13 judges formed the Kesavananda bench.
- Nani Palkhivala, Fali Nariman and Soli Sorabjee have filed a complaint against the government.
The consequences of the case
- Indira’s government defended itself from the Kesavananda verdict. The Chief Justice of the Indian Supreme Court, S M Sikri, retired the day after the verdict and was replaced on April 26, 1973 by Justice A N Ray, who was one of six dissenting justices. Judge Ray became the fourteenth CJI to replace Justices Shelat, Grover and Hegde, who sided with the majority in the case.
- Attorney General Niren De proposed to the Supreme Court without even filing a petition for review, and CJI Ray, as master of the roster, assembled a bench of 13 justices to review the verdict.
- However, on November 12, 1975, the bank was dissolved after CJI Ray gave in to immense social pressure.
- Since then, the basic structure doctrine has been applied to a number of important Supreme Court cases, notably SR Bommai (1994), when the Supreme Court upheld the indictment of the President of the BJP governments following the demolition of the Babri Masjid , citing a threat of secularism from these governments.
- Critics of the doctrine have called it undemocratic, because unelected judges can invalidate a constitutional amendment. But, in general, it has been hailed as a brake against majoritarianism and authoritarianism.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Kaziranga National Park got additional area
The government of Assam approves the addition of 3,053 hectares in two districts
Table of Contents
ToggleThe government of Assam has approved the addition of 30.53 square kilometers to the 884 square kilometers of Kaziranga National Park. The additional areas straddling two districts, Nagaon and Sonitpur, would bring the larger Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve (KNPTR) to 1,085.53 square kilometers. However, wildlife habitat still awaits possession of 14.62 square kilometers previously “added” in two other districts. The core area of the KNPTR is 430 square kilometers. A spokesperson for the Forestry Department said the preliminary notifications were for the seventh, eighth and ninth additions on Thursday.
“The additions include areas vacated by invasion and suitable wildlife habitat on river islands (sandbanks) which are vulnerable to invasion. This is a movement to consolidate wildlife areas in anticipation of better conservation of wildlife and reduction of negative interactions between humans and wildlife in the future, ”
said the director of KNPTR, P. Sivakumar.
He added that the three additions are habitat corridors and would help provide connectivity to Orang and Nameri National Parks across the Brahmaputra River from KNPTR in addition to the Karbi Anglong Hills in the south of the park, where rhinos, tigers, deer and others animals roam during floods.
- The seventh and eight additions totaling 4.83 square kilometers are in Nagaon District, while the ninth, covering 25.70 square kilometers, is in Sonitpur District.
- Wildlife activists appreciated the official stamp on the KNPTR expansion, but noted that rhino habitat has yet to be returned to possession of 1,461.59 hectares (14.62 square kilometers) of land Comprising the second, third, fifth and sixth additions in the districts of Golaghat and Biswanath.
- On August 17, the High Court in Gauhati ordered the Chief Conservator of Forests (Wildlife) and the Chief Wildlife Warden, Assam, to report on the steps taken for the eviction of invaders in areas previously added to the park.
- The court ordered on October 9, 2015 the eviction of the usurpers in the second, third, fifth and sixth additions to the KNPTR, while observing that the state government had handed over a total of 39,836.74 hectares covering the additions. first and fourth.
- Designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985, the KNPTR has approximately 2,413 rhinos and 121 tigers.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Kaushik Basu, an Indian economist receives prestigious
The Alexander von Humboldt Foundation awarded the Humboldt Research Prize to Indian economist Kaushik Basu on Tuesday.

Kaushik Basu, an Indian economist receives prestigious Humboldt research award
Table of Contents
ToggleIndian economist Kaushik Basu received the Humboldt Research Award for Economics. The award was presented to him by Professor Dr. Hans-Bernd Schäfer from the Bucerius Law School in Hamburg, Germany. Kaushik Basu, Indian economist and professor at Cornell University, USA, received the Humboldt Research Award for Economics.
- Basu was born and raised in Calcutta and educated at the University of Delhi and the London School of Economics. He was Senior Vice President and Chief Economist at the World Bank from 2012 to 2016, before serving as Chief Economic Advisor to the Government of India for three years.
- Professor Basu is the author of several articles on economics and a play. He also received the Padma Bhushan, the third highest civil honor bestowed by the Indian government.
- He lives in New York where he teaches economics and international studies at Cornell University. He identifies himself as belonging to the New Keynesian economics school of thought. Kaushik Basu was nominated for his award by Professor Hans-Bernd Schäfer from Bucerius Law School, Hamburg, Germany.
- In order to promote international scientific cooperation, the winners of the Humboldt Research Prize are invited to carry out research projects of their choice in cooperation with fellow specialists in Germany. Basu said he plans to use the award to research moral philosophy and game theory, as well as law and economics, the Cornell Chronicle reported.
Who is Kaushik Basu?
- Kaushik Basu, former chief economist at the World Bank (2012-2016), is currently a professor of economics at Cornell University. He was also Chief Economic Advisor to the Government of India from 2009 to 2012.
- Previously he has also received the Padma Bhushan, India’s third highest civil honor.
- A graduate of the London School of Economics, Mr. Basu is the current president of the International Economic Association.
- He has written several articles, including “Introduction: The state of the economy, the state of the world”, “Individual preferences and democratic processes: two theorems with implications for electoral politics”, “Inequality, growth, poverty, lunar eclipses: Politics and arithmetic ‘.
About the Humboldt scholarship
- The prestigious Humboldt Research Award is sponsored by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. It is awarded to no less than 100 beneficiaries each year.
- The award honors economists and scientists from around the world for their work and includes a cash prize of € 60,000.
- There is also an offer to carry out research projects at a scientific institution in Germany for a maximum period of 12 months.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Kashmiri saffron got GI Tag
Kashmiri saffron is considered to be of the highest quality in the whole world, it is different from saffron in other countries. kashmiri saffron is considered superior in qualities with high medicinal value due to its high aroma, dark color, long and thick thread (stigma).
Table of Contents
Toggle
Where Kashmir Saffron Produced?
Kashmir mainly produces 3 types of saffron, Gucchi saffron, Lachha saffron and Mongra saffron, its production in Kashmir circa 1st century BC. Produced from, the production of Kashmiri saffron is the only saffron grown at an average height of 1600 m to 1800 m above sea level. It is mainly produced in Pulwama, Budgaon, Kistwar and Srinagar.
The largest saffron-producing country in the world is Iran which cultivates more than 300 tonnes of saffron on 30,000 hectares of land every year. Apart from this, Spain and Afghanistan sell saffron of poor quality, due to which the price of Kashmiri saffron has fallen by almost 50%. Since But due to the low quality saffron of Iran and other countries, Kashmiri saffron producers are suffering a lot of losses. Therefore, Kashmiri saffron growers want their saffron to be distinguished in the world so that they get a good price for good quality saffron.
Benefits of GI Tag to Kashmiri Saffron:
After getting the Kashmir Tag to Kashmiri Saffron, the producers here can write in their packaging that it is a Kashmiri product i.e. it is of high quality and hence people will be convinced that for this product It is also not wrong to pay a high price, thus getting the GI tag will create a distinct identity of Kashmiri saffron in the market, increase sales and it will also be beneficial to produce.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
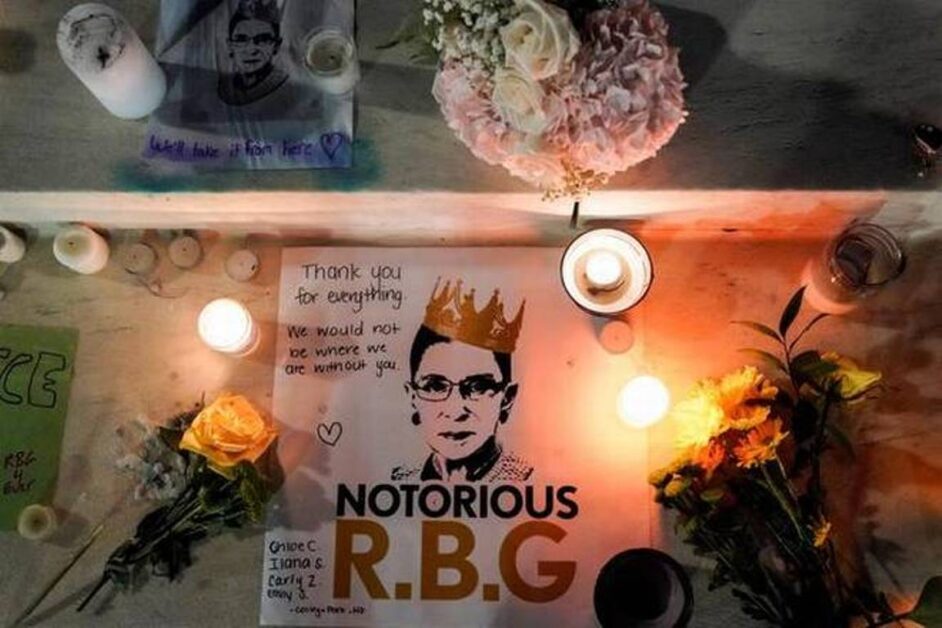
Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg demise
Supreme Court Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg has moved slowly. When the court was in session, she often had her head tilted, which sometimes made visitors believe that she was asleep.
Table of Contents
Toggle- She once admitted that she nodded his head sometimes. She once confessed to falling asleep during a State of the Union. But it was a mistake to equate his gait and gaze with fragility, as Ginsburg has repeatedly demonstrated a fierce resistance to personal loss and the serious health issues that made the little New Yorker a great champion of the world women’s rights and a strong presence at court over 27 years.
- She made few concessions on age and recurring health issues, and she worked regularly with a personal trainer. She never ran out of time out of court until the age of 85, and only after surgery in December 2018 for lung cancer.
- Ginsburg died of complications from metastatic pancreatic cancer at her Washington home on Friday at the age of 87, the court said. Upon completion of his tenure, she became a social media icon, Notorious RBG, a name coined by a law student who admired Ginsburg’s dissent in a case violating major civil rights laws.
- Justice was initially surprised. There was nothing remarkable about this standing lady who wore a variety of lacy necklaces on the bench and often appeared in public with stylish gloves on.
- But when her employees and grandchildren explained the connection to fellow Brooklyn rapper, The Notorious B.I.G., their skepticism turned into ecstasy.
- In the words of today’s generation, that’s great, Ginsburg said in 2016, shortly before his 83rd birthday. In her final years at court, Ginsburg was the undisputed leader of liberal judges, as openly dissenting as he was cautious in years past.
- Criticizing the Conservative majority in court for dropping a key part of the historic franchise law in 2013, Ginsburg wrote that it was like throwing his umbrella into a storm because she didn’t they are not wet.
- Her stature on the court and the death of her husband in 2010 likely contributed to Ginsburg’s decision to stay on the bench beyond the goal he had originally set for himself, to match Judge Louis, aged 22 years old. Brandeis in the field and his retirement at 82.
- A woman, a mother and a Jew: Ginsburg had a special affection for Brandeis, the first Jew appointed to the high court. She was the court’s second wife and its sixth Jewish judge.
- Eventually, she was joined by two other Jews, Stephen Breyer and Elena Kagan, and two other women, Kagan and Sonia Sotomayor. Both of these developments were perhaps unthinkable when Ginsburg graduated from law school in 1959 and faced the three-fold scarecrow of finding employment as a woman, mother and Jew.
- Forty years later, she noted that religion had become irrelevant in the selection of Superior Court judges and that gender was on the same lines, even though she was asked how many women would suffice for the High Court.
- Ginsburg answered without hesitation; She could take credit for gender equality in law. In the 1970s, she argued six key cases in court when she was the architect of the women’s rights movement, she won five.
Equality for Women: Ruth Bader Ginsburg doesn’t need a Supreme Court seat to earn a place in the history books of the United States, President Bill Clinton said in 1993 when she announced her nomination. She already did.
- Her stint as a judge was marked by triumphs for women’s equality, as in her opinion the court which ordered the Virginia Military Institute to accept women or forgo its public funding. There have also been setbacks.
- She strongly opposed the 2007 court ruling to uphold the nation’s ban on an abortion procedure that opponents call partial birth abortion.
- The alarming decision, Ginsburg said, can only be understood as an effort to undermine a right repeatedly stated by this court, and with a growing understanding of its centrality in the lives of women.
“I thought I could do the job of a lawyer better than anyone,” he writes. “I have no artistic talent, but I write pretty well and clearly analyze the themes.”
Ginsburg once said that she did not go into law as an equal rights advocate.
Liberal leaning: Besides civil rights, Ginsburg took an interest in the death penalty, voting several times to limit its use. During her tenure, the court ruled unconstitutional for states to execute people with intellectual disabilities and murderers under the age of 18.
- Then later with the two people appointed by President Barack Obama, Sotomayor and Kagan. In the more controversial cases, Ginsburg often disagreed with the more conservative members of the court.
- However, she was personally the closest in court to Judge Antonin Scalia, her ideological opposite. He once explained that he viewed Scalia’s sometimes scathing dissent as a challenge.
- “How am I going to answer this question in a truly disapproving way?” She said. Scalia died in 2016. Regarding her own dissent, Ginsburg said some were aimed at influencing the opinions of other judges, while others have appealed to the intelligence of another day in the hope that they could provide information advice future courts.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
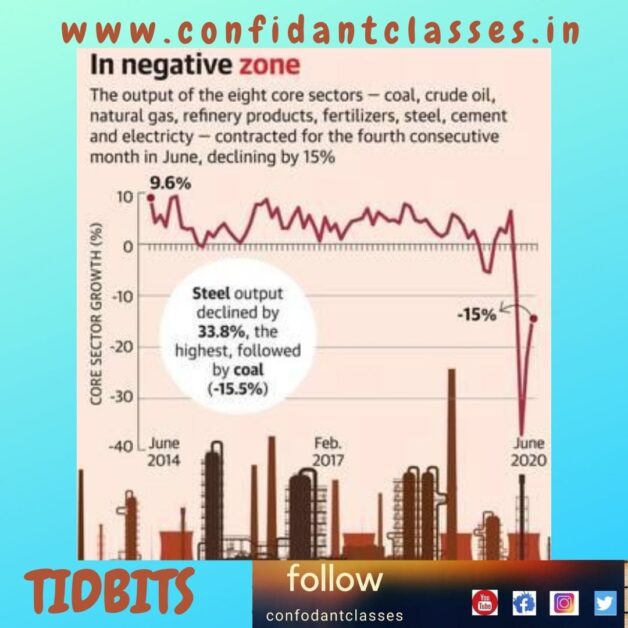
June 2020 output of core industries
Output from eight core sector industries fell for the fourth consecutive month in June 2020, although the contraction decreased to 15%, showing some recovery from the 22% drop in May, according to data released Friday by the Commerce Department. Economists expect the negative trend to continue for at least two more months.
Table of Contents
Toggle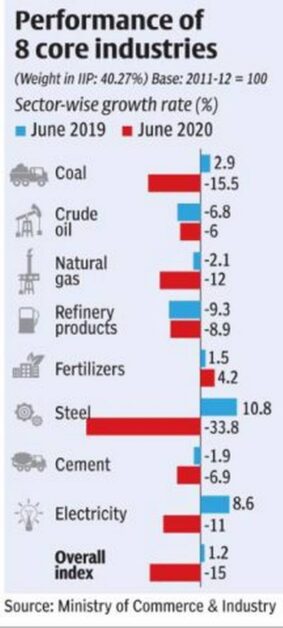
- In April-June 2020-21, the sector’s production fell 24.6% compared to a positive growth of 3.4% in the same period of the previous year.
- Among the eight key sectors, the fertilizer industry was the only one to experience real growth in June, with production up to 4.2% since June 2019. This, however, is less than the 7.5% growth in May 2020, but reflects prospects in the agricultural sector where a normal monsoon leads to expectations of an excellent kharif harvest.
- Other industries registered a contraction, with the steel sector as the worst, with a 33% drop in production the previous year.
- Cement production fell almost 7%, despite a 22% improvement in contraction seen in May.
- The energy sectors also registered negative growth, with coal production of 15.5% and crude oil and natural gas production of 6% and 12% respectively.
- Oil refinery output, which weighs the highest in the central sector index, contracted by almost 9%, while electricity production fell 11%.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
JUDICIAL SERVICES SYLLABUS STATE WISE
The Judicial Service Examination consists of two levels and a Viva Voce test. The first examination is the Judicial Service Preliminary Examination and the next one is the Judicial Service Mains Examination. The candidates shortlisted from the prelims will be eligible to appear for the Main exam. The final merit list is based on both these levels along with the marks obtained in the personality test. Certain states have a requirement of minimum marks in the viva voce test, whereas other states aggregate it to the marks of the Mains and prelims.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Read Also: Top Law Classes in Delhi
List of Judiciary Exams in India
| List of Organisations | Exam Category | Minimum Eligibility |
| Bihar District Judge | High Court of Patna Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law, Post-graduation Degree in Law |
| Delhi Junior Judicial Assistant | Delhi High Court Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Karnataka State Oath Commissioner | High Court of Karnataka Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Tamil Nadu District Judge | Madras High Court Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Tamil Nadu Civil Judge | Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Civil Judge of Maharashtra | Maharashtra Public Service Commission (MPSC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Patna Judge Personal Assistant | High Court of Patna Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Uttarakhand Civil Judge | Uttarakhand Public Service Commission (UKPSC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Gujarat Civil Judge | High Court of Gujarat Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Jharkhand Civil Judge (Junior Division) | Jharkhand Public Service Commission (JPSC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Judicial Services | High Court of Delhi Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Madhya Pradesh Civil Judge | Madhya Pradesh High Court Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Civil Judge of Jammu and Kashmir | Jammu & Kashmir Public Service Commission (JKPSC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Chhattisgarh District Judge | High Court of Chhattisgarh Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Uttar Pradesh District Judge | Allahabad High Court Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Gujarat Civil Judges | High Court of Gujarat Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Karnataka State District Judge | High Court of Karnataka Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Civil Judge in West Bengal | West Bengal Public Service Commission (PSCWB) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Madhya Pradesh District Judge (Entry Level) | High Court of Madhya Pradesh (MPHC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Gujarat Civil Judge | High Court of Gujarat Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Delhi Judicial Service | Delhi High Court Examination Council Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Karnataka Civil Judge | High Court of Karnataka Exam | Member of BCI, and Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Rajasthan Court Commission | Rajasthan High Court Civil Judge | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Delhi Junior Judicial Assistant | Office of The District & Sessions Judge, Delhi | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Madhya Pradesh Civil Judge | Madhya Pradesh High Court (MPHC) | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Himachal Pradesh High Court Service Commission | Clerks, Junior Office Assistants & Process Servers vacancies | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Bihar Provincial Civil Services | Bihar PCS Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Chhattisgarh Public Service Commission State Service Exam | Judiciary Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law, and a minimum of two years’ experience as an advocate |
| Himachal Pradesh Administrative Services Combined Competitive Exam | Competitive State Exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
| Rajasthan Administrator Services Exam | State Level administrator exam | Bachelor’s Degree in Law |
A total of 24 states in India conducts the judicial services exam. The eligibility criteria, exam pattern, pay scale, the recruitment process of all states differs.
Syllabus for Preliminary examination
The preliminary examination generally consists of questions from the following subjects:
- General Knowledge and Current Affairs
- Proficiency In English Language and Aptitude
- Constitutional law
- IPC, CPC, CrPC and The Indian Evidence Act
- Contract Law and Tort Law
- Transfer of Property law
Apart from these, some states cover certain other topics in their syllabus as follows
- Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Maharashtra, Manipur, and Nagaland: Proficiency in the official language of Assam
- Bihar: Elementary general Science, Administrative law, Hindu and Muslim personal laws, Principles of Equity, Law of trusts, Specific Relief Act, Commercial law.
- Chhattisgarh: Accommodation Control Act, Court fees act, Registration Act and Chhattisgarh Land revenue code, Limitation, and Specific relief acts.
- Delhi: Principles Governing Arbitration Law, the Partnership Act.
- Goa: Sales of Goods Act, Land laws of Goa, The Scheduled Tribe and Scheduled Caste (Prevention of Atrocities Act, 1989).
- Karnataka: Karnataka Rent Act.
- Kerala: Kerala Building (Lease and Rent Control) Act.
- Madhya Pradesh: Madhya Pradesh Accommodation Control Act, Madhya Pradesh Land Revenue Code.
Syllabus for the Main examination: The syllabus for the Main examination of Judiciary also varies according to each state. The patterns are as follows:
Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram, Maharashtra, and Jammu & Kashmir
- Paper I (To test English; 100 marks, 2 hours): Essay, precise writing, Grammar.
- Paper II (To test General Knowledge; 100 marks,2 hours): Objective test, Aptitude Test.
- Paper III (Law; 100marks, 2 hours): Transfer of Property, Civil procedure code, Indian Contract Act, Constitution of India.
- Paper IV (Law; 100 marks, 2 hours): Indian Penal Code, CrPC, Law of Torts, Indian Evidence Act.
Bihar
- Part I: Compulsory Paper- General knowledge including current affairs (150 marks), Elementary Science (100marks), General Hindi (100 marks ), General English (100 marks), Law of evidence and procedure (150 marks) Hindi and English are compulsory papers but only qualifying in nature which requires only 30 marks out of 100.
- Part II: Optional paper(150 marks each)- Constitutional Law of India and England(, Hindu and Muslim Law, Transfer of property, Principles of Equity, Law of trusts and Specific Relief Act, Law of Contract and Torts, Commercial law
Chhattisgarh
- Framing of issues and writing of judgment in Civil Cases (40 marks)
- Framing of charges and writing of judgment in Criminal Cases (40marks)
- Translation: English to Hindi (10marks), Hindi to English(10marks)
Delhi
- Paper I: General Knowledge and Language (250 marks) – Current affairs, Essay, Translation, and precise writing.
- Paper II: Civil Law I( 200 marks)- Indian Contract Act, Indian Sale of Goods Act, Indian Partnership Act, Specific Relief Act, Hindu Law, Muslim Law, Delhi Rent control Act and Law of Torts.
- Paper III: Civil law II (200 marks)- Civil Procedure Code, Law of evidence, Law of Limitation and Law of Registration.
- Paper IV: Criminal Law (200 marks) -Criminal Procedure Code, Indian penal code and Indian Evidence Act
Goa
- Paper I: The Indian Contract act, 1872, The Specific Relief Act, 1963, The Limitation Act, 1963, Sales of Goods Act, 1930, Indian Partnership Act, 1932, The Code of Civil Procedure Code, 1908, Transfer of Property Act, 1882, The Easement Act,1882, Family Laws in Goa , Land Laws in Goa.
- Paper II: The code of Criminal procedure Code, 1973, The Indian Penal Code, 1860 The Evidence Act, 1872, The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989, The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, Essay on Current Legal Topics
Haryana and Punjab
- Paper I: Civil Law I( 200 marks)-Code of Civil procedure, Punjab Courts Act, Indian Contract Act, Indian Sale of Goods Act, Indian Partnership Act, Specific Relief Act.
- Paper II: Civil Law II (200 marks)- Hindu Law, Muslim Law and Customary Law, Law of Registration and Limitation.
- Paper III: Criminal Law (200 marks)- Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal procedure, Indian Evidence Act.
- Paper IV: English- Essay (25 marks), Words and phrases (25 marks), Comprehension (25 marks), Corrections (25 marks).
- Paper V: Language- Hindi in Devanagari Script (100/150 marks)
Himachal Pradesh
- Paper I: Civil Law I( 200 marks)-Code of Civil procedure, Indian Stamp Act, Indian Evidence Act, Himachal Pradesh Courts Act, Specific Relief Act
- Paper II: Civil Law II (200 marks)- Indian Contract Act, Hindu Law, Transfer of Property Act, Himachal Pradesh Urban Rent Control Act, Indian Limitation Act.
- Paper III: Criminal Law (200 marks)- Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal procedure, Chapter XVII of Negotiable Instruments Act, HP Excise Act, Wildlife Protection Act, Indian Forest Act.
- Paper IV: English Composition (200 marks).
- Paper V: Language (100 marks)
Jharkhand
- Paper I: Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal Procedure Code, Indian Evidence Act, Limitation Act.
- Paper II: Civil Procedure Code, Transfer of Property, Indian Contract Act, Sales of Goods Act, Arbitration and Conciliation Act.
- Paper III: Hindu Law, Muslim Law, Rent Control Law, Specific Relief Act, and Jurisprudence.
- Paper IV: Hindi and English.
Karnataka
- Paper I: Translation Paper (100 marks) – Depositions, Judgments, and Documents.
- Paper II: Law paper I (100 marks) – Civil procedure Code, Criminal Procedure Code, Indian Evidence Act, Principles of Pleading and Indian Constitution.
- Paper III: Law paper II (100 marks) – Framing of issues and writing judgments in civil cases.
- Paper IV: Law paper III (100 marks)-Framing of charges and writing judgments in criminal cases
Kerala
- Paper I: English Grammar, General Essays, Translation of Malayalam Documents and Depositions to English, Precise writing.
- Paper II: Indian Contract Act, Transfer of Property, Limitation Act, Specific Relief Act, Easements Act, Kerala Building Act, Hindu Succession Act, Indian Succession Act, Dissolution of Muslim Marriage Act, Kerala Court Fees and Suits Valuation Act, Kerala Stamp Act, Legal Services Authorities act, The Kerala Panchayatha Raj Act, Kerala Municipality Act, Negotiable Instruments Act and Registration Act
- Paper III: Indian Penal Code, Indian Evidence Act, Abkari Act, Negotiable Instruments Act, the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, Juvenile Justice Act, Kerala Police Act, Probation of Offenders Act, Forest Act, NDPS Act.
- Paper IV: Code of Civil Procedure, Civil Rules of Practice, Kerala Civil Courts Act Code of criminal procedure, Criminal Rules of Practice, Framing of charges and issues, Judgment writing.
Madhya Pradesh
- Paper I: Civil Law and procedure.
- Paper II: Criminal law and procedure.
- Paper III: Writing Skill, Court Practice, Translation, and Current Legal Knowledge
- Paper V: Judgment writing.
Odisha
- Paper I: General English.
- Paper II: Procedural laws- Civil procedure code, Criminal procedure code, Indian Evidence Act.
- Paper III: Optional papers- Law of Crime and Law of torts, Hindu and Muslim Law, Law of property, Law of Contract, Jurisprudence, and Constitution of India
Rajasthan
- Paper I: Law paper I- Constitution of India, Civil procedure Code< Contact law, Tort laws, Motor vehicle law, Rent control law, Personal laws, Law of Transfer of Property
- Paper II: Law paper II- Criminal law, Narcotic Law, Law relating to cybercrimes and electricity theft, Law of probation, Law on juvenile delinquency.
- Paper III: Language paper I- Hindi essay writing and grammar
- Paper IV: Language paper II- English essay writing, translation, and grammar
Sikkim
- Paper I: Procedural law, Local law, Indian evidence Act, Limitation Act
- Paper II: Hindu Law, Contract law, Sales of goods act, Partnership Act, Specific Relief Act, General Clauses Act, transfer of property Act, Indian Penal Code, Constitutional law
Uttarakhand
- Paper I: Substantive Law
- Paper II: Evidence and procedure
- Paper III: Revenue and criminal law
- Paper IV: The present-day- Current affairs and general knowledge
- Paper V: Language
Uttar Pradesh
- Paper I: General knowledge- History of India and Indian Culture, Geography of India, Indian Polity, Indian economy, international affairs.
- Paper II: Law- Jurisprudence, International Organizations, Indian constitution, Transfer of property, Indian Evidence Act, Code of criminal procedure, Code of Civil procedure, Contract laws
West Bengal
- Paper I: Compulsory papers- English composition, Bengali, general knowledge, Civil law, Criminal law, Contract law, Transfer of Property Act
- Paper II: Optional papers- Hindu law, Muslim law, Jurisprudence and principles of legislation, Laws relating to companies and insurance, Law of trusts and Specific relief, Partnership Act, Law of limitation, Constitutional law.
Faculties

1. RAJESH RANJAN: IPC, CRPC, CPC, CONTRACT ACT, EVIDENCE ACT, CONSTITUTIONAL LAW, NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT, INTERNATIONAL LAW, TRANSFER OF PROPERTY ACT, HINDU LAW, MUSLIM LAW, PARTNERSHIP ACT, JUDGMENT WRITING
2. NAINA SEHGAL: SPECIFIC RELIEF ACT, RENT CONTROL ACT, LIMITATION ACT, INDIAN EASEMENT ACT, TRUST ACT, SALE OF GOODS ACT, LAW OF TORTS
3. GS and CURRENT AFFAIRS when notification comes
4. ESSAY: RAJESH RANJAN, SUNIL SINGH
5. TRANSLATION: AKHILESH MISHRA
6. ENGLISH: RAJESH RANJAN
7. LOCAL LAWS: When notification comes teachers of respective states are invited to conduct classes.
REGULAR BATCH:
- 4 hrs Monday to Friday
- Saturday: GS and Misc.
- Total course length 9 months (approx)
- Fees: 35000/ plus GST
STUDY MATERIALS
- BOOKLETS OF SUBSTANTIVE LAWS + PROCEDURAL LAWS EXCEPT CrPC, CPC, LOCAL LAWS, GS , ESSAY, TRANSLATION, ENGLISH
- HANDOUTS OF LATEST SUPREME COURT JUDGMENTS WITH ANALYSIS BY RESPECTIVE FACULTIES.
- EXHAUSTIVE CLASSROOM DICTÀTION
Read Also:
- All India Judicial Services | AIJS
- Career Avenues in Judicial services
- NLSIU Bengaluru to launch three-year interdisciplinary LLB for graduates
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
JMI starts entrance exams for various programs
Jamia will direct a total of 20 programs under CUET: 15 undergraduate programs and five graduate programs. Admissions for all remaining programs will be made by the institute.
Jamia Millia Islamia began today the entrance exams to various programs for the 2023-24 academic session. The entrance examinations for the Master of Media Governance, Master of West Asian Studies, Master of Chemistry, Master of Biophysics, PG Diploma in Drama, PG Diploma in Still Photography, and Diploma in Engineering were held today. Nearly 3,000 candidates took the exam.
Jamia will direct a total of 20 programs under CUET: 15 undergraduate programs and five graduate programs. Admissions for all remaining programs will be made by the institute. The undergraduate courses for which admissions will be made under the CUET are BA (Hons) Turkish Language and Literature, BA (Hons) Sanskrit, BA (Hons) French and Francophone Studies, BA (Hons) Spanish and Latin Studies, BA (Hons) Korean Language, BA (Hons) History, BA (Hons) Hindi, BA (Hons) Urdu, BA (Hons) Persian, BA (Hons) Economics BSc Biotechnology, BVoc (Solar Energy), BSc (Hons) Physics , BSc (Hons) Chemistry and BSc (Hons) Applied Mathematics.
Read Also:
JK-IGRAMS
Deputy Governor of Jammu and Kashmir (GG) Manoj Sinha on Friday launched the Jammu and Kashmir Integrated Complaints Tracking and Resolution System (JK-IGRAMS), with the aim of engaging with the public and focus on governance issues in the union territory.
Table of Contents
Toggle- First in three districts, the system is being tested in Jammu, Srinagar and Reasi – and will be rolled out gradually to the remaining districts by October 2.
- It will replace the current portal launched in 2018.
- It will be available 24 hours a day with authentication by the applicant’s prosecution, acknowledgment of receipt by the applicant at each stage, comments from the applicant and presentation of complaints via the call center by making a phone call between 9:30 a.m. and 10:00 p.m. 5:30 pm every day except Sunday.
- It has now been integrated down to the district level by mapping nearly 1,500 public offices in 20 districts of the Union.
- The measure comes at a time when the feeling of disconnection and alienation is growing among the population, especially in the Kashmir Valley, which has remained at the forefront since the revocation of J&K special status last year.
Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile
AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide
NLSIU Bengaluru to Launch 3-Year BA (Hons) Programme in 2025 | Key Details
CUET-UG to Be Fully Online: Key Changes Announced by UGC
D.Pharma Course in India | Careers After Class 12th
The Draft UGC (Minimum Standards of Instructions in the Award of UG and PG Degrees) Regulations 2024 | A Comprehensive Overview
Recent Posts
- Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB)

- Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026

- CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today

- The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis

- IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile

Categories
Recent Posts
- Your Comprehensive Guide to the Common University Entrance Exam LLB (CUET LLB) 21st December 2024
- Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026 21st December 2024
- CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today 20th December 2024
- The Surge in Indian Students Studying Abroad | A Five-Year Analysis 20th December 2024
- IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile 20th December 2024
- AIBE 19 Exam 2024 | Complete Guide 19th December 2024