Bihar regiment bravely fought in the recent clash with the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in the Galwan Valley of Ladakh, losing 12 soldiers, including the commander of his 16th battalion, Colonel Bikkumalla Santosh Babu. The regiment has several achievements and victories on the battlefield against its name and has been at the forefront of many successful military operations.
The crest of the Bihar regiment contains three-headed Ashoka lions, which was chosen by the commander of the 1st Battalion of Commander Bihar, Captain M Habibullah Khan Khattak in 1941. This regiment made an important contribution to the protection of India against its enemy, its acts of immense courage and courage have Glory added to the pages of the Indian army.
An overview of the history of the Bihar regiment
The Bihar regiment was created by the British East India Company under the name of “Native Bengal Infantry”. In fact, the British were so impressed by the courage and tenacity of the Bihari soldiers that in 1758, when Lord Robert Clive became the first British governor of the Bengal presidency, the 34th Sepoy Battalion was raised in its entirety with soldiers recruited from the Bhojpur district of Bihar.
The other areas in which the soldiers were recruited mainly included the Shahabad and Munger districts of present-day Bihar. These troops won spectacular victories during the Buxar, Karnatic and Maratha wars.
They have even proven themselves abroad in Malaysia, Sumatra and Egypt. But Bihari’s troops also showed their fearless attitude and their strict principles by being the first to rebel against the introduction of greased cartridges and to prefer to be exploited by pistols rather than to lose confidence during the first war of independence of India (1857).
Fearing their war capabilities and the damages they caused during the First War of Independence in 1857, the British disbanded the 18 Bihar battalions and all state recruitment was halted.
Babu Kunwar Singh and Birsa Munda are the two legendary figures in the struggle for independence. While Babu Kunwar Singh was one of the heroes of 1857, Birsa Munda, from the Munda tribe of present-day Jharkhand, had a bad time for the British.
Large-scale recruitment of Bihar soldiers started again during the Second World War and they joined the 19th Hyderabad Regiment 1. The Bihar Regiment was created on September 15, 1941 and owes its origin to 11/19 of the Hyderabad Regiment.
The battalion received two “battle honors” during World War II, namely “Haka” and “Gangaw” and also received Burma’s “theater of honor 2”.
Bihar also fought with distinction in Malaysia as part of the “LIGHT CLOSING FORCE” under Lieutenant Colonel (later Lieutenant General) Sant Singh.
The regiment also participated in the Indo-Pakistan Wars of 1965 and 1971 and performed the assigned tasks commendably. The 1st Bihar Regiment Battalion participated in Operation Vijay during the Kargil War on Pakistan in 1999.
The Bihar regiment took over Jubar Hill and Tharu from the Pakistanis and received the head of the military personnel unit. Citation, Honor Battle “Batalik” and Honor “Kargil”.
Several battalions of the Bihar Regiment participated in United Nations peacekeeping missions, including 1 Bihar in Somalia (1993-1994).
Troops of 10 Bihar, 5 Bihar and 14 Bihar were part of United Nations peacekeeping operations in the Congo in 2004, 2009 and 2014, respectively.
The Bihar Regiment also has four Rashtriya Rifle Battalions (4RR, 24RR, 47RR, 63RR), which is among the largest units of all Indian Army regiments.
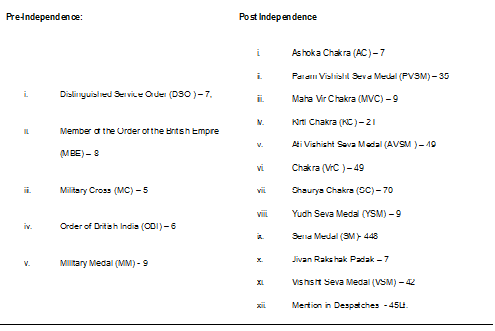
One of the highly decorated Indian Army regiments, the Bihar Regiment soldiers have won the following awards to date (June 22, 2020):











More Stories
Delhi University to Launch One-Year Postgraduate Programme in 2026
CLAT 2025 Counselling Registration Window Closes Today
IIM CAT Result 2024 | 14 Candidates Score Perfect 100 Percentile