The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced the drop in performance of the government’s new 10-year security bonds to 5.79%, the lowest since February 2009. This reflects aggressive rate cuts and central bank liquidity injection.
In post-issue trading, the bond closed at 5.72% at the price of Rs. 100.55. While the G-sec auction was announced for Rs.10000 crore , the RBI exercised the option of green shoes for Rs.2000.
The new bond yield of 6.45% in 2029, which was the previous benchmark, forced a readjustment of the prices of all existing government bonds, leading to capital gains for bond holders. Bond prices and yields are moving in opposite directions. RBI cut rates by 210 basis points in 16 months and also took several steps to manage long-term liquidity and returns.
Falling 10-year government bond yields showed that bond investors expected future demand for money to drop. That is why future interest rates should be lower. In turn, a drop in the demand for money in the future will only occur when growth slows further. Therefore, the decline in government bond yields generally suggests that economic actors “expect” growth to slow down in the future. Of course, bond yields simply “suggest” that they do not “slow down” future growth.
What are bonds?
A bond is an instrument for borrowing money. It’s like a promissory note. A bond could be issued / issued by the government of a country or by a fundraising company. Since government bonds (called G-sec in India, Trésor in the United States, and Gilts in the United Kingdom) come with a sovereign guarantee, they are considered one of the safest investments. As a result, they also give the lowest returns on investment (or returns). Investments in corporate bonds tend to be more risky because the chances of failure (and therefore the chances that the company will not repay the loan) are greater.
What are bonds yields?
Simply put, the yield on a bond is the effective rate of return it earns. But the rate of return is not fixed, it changes with the price of the bond. Each bond has a face value and a coupon payment. There is also the price of the bond, which may or may not be equal to the face value of the bond.
Suppose that the face value of a 10-year G-sec is 100 rupees and that your coupon payment is 5 rupees. Buyers of this bond will give the government 100 rupees (face value); in exchange, the government will pay them 5 rupees (coupon payment) each year for the next 10 years and reimburse their 100 rupees at the end of the term. In this case, the yield on the bond, or effective interest rate, is 5%. Return is the investor’s reward for parting with Rs 100 today, but for running out of it for 10 years.
Why and how do yields go up and down?
Imagine a situation where there is only one bond and two buyers (or people willing to lend to the government). In such a scenario, the sale price of the bond can go from Rs 100 to Rs 105 or Rs 110 due to the competitive offers of the two buyers.
Above all, even if the bond sells for Rs 110, the coupon payment of Rs 5 will not change. Consequently, as the price of bonds increases from Rs 100 to Rs 110, the yield drops to 4.5%. Likewise, if the economy-wide interest rate is different from the initial coupon payment promised by a bond, market forces will quickly ensure that the yield aligns with the interest rate of the economy.
In this sense, G-sec yields are closely synchronized with the interest rate prevailing in an economy. Referring to the example above, if the interest rate in effect is 4% and the government announces a bond with a yield of 5% (i.e. a nominal value of 100 rupees and many 5 rupees), many people will rush to buy this bond to earn a higher interest rate. This surge in demand will start to raise bond prices, even if yields fall.
This will continue until the bond price reaches Rs 125, at that time, a coupon payment Rs-5 would be equivalent to a yield of 4%, the same as in the rest of the economy. This process of aligning yields with the prevailing interest rate in the economy works in reverse when interest rates are higher than the yields originally promised.
And what is a yield curve, and what does it signify?
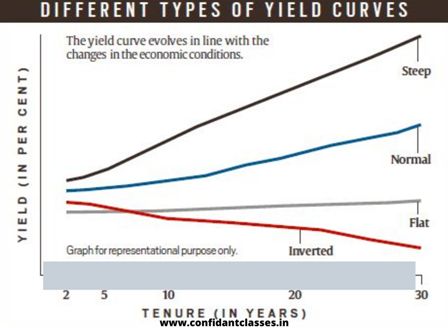
A yield curve is a graphical representation of bond yields (with an equal credit rating) across different time horizons. Generally, the term is used for government bonds, which come with the same sovereign guarantee.
If bond investors expect the US economy to grow normally, they would expect to receive more rewards (that is, get more returns) when they lend for a longer period. This results in a normal yield curve, with an upward slope (see graph). The steepness of this yield curve is determined by the speed at which an economy is expected to grow. The longer you expect it to grow faster, the higher the performance for longer durations. When the economy is expected to grow only marginally, the yield curve is “flat.”
What then is yield inversion, and what does it mean?
Performance reversal occurs when the return on a longer holding link becomes lower than the return on a shorter holding link. It also happened last week when the 10-year Treasury yield fell below the 2-year Treasury yield.
A performance investment generally announces a recession. An inverted yield curve shows that investors expect a sharp fall in future growth; In other words, the demand for silver would be much lower than it is today, and therefore the returns are also lower. A yield inversion has always been followed by a recession.









More Stories
Orissa High Court Criticizes OPSC for Flawed Evaluation in Judicial Exam
MAH CET Registration 2025: Extended Deadline and Key Details
CUET PG 2025 Registration Extended: Apply Before February 8