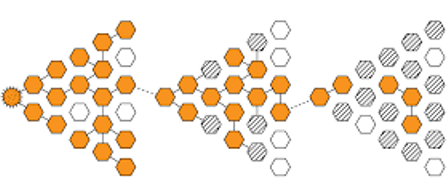
When the majority of the population is immunized against an infectious disease, Herd immunity provides indirect protection, or collective immunity, to those who are not immunized against the disease. For example, if 80% of a population is immune to a virus, four out of five people who meet someone with the disease will not get sick or spread it further.
Simply 70 to 90% of the population generally needs immunity to achieve herd immunity. Measles, mumps, polio, and chickenpox are examples of infectious diseases that were once very common, but are now rare in the United States because vaccines have helped develop collective immunity.
Sometimes we see outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases in communities where vaccination coverage is lower because they do not benefit from protection of the herd. For infections without a vaccine, despite the fact that many adults have developed immunity from a previous infection, the disease can still circulate among children and infect those whose immune systems are weakened. This has been seen in many of the above diseases before the development of vaccines. Other viruses like the flu mutate over time, so antibodies from a previous infection only offer protection for a short time, or the flu, it’s less than a year.
If SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is like other corona viruses that currently infect humans, we can expect infected people to be immune for months or even years, but probably not their entire lives. As with any other infection, there are two ways to achieve herd immunity.
A large part of the population is infected or receives a protective vaccine, it is likely that at least 70% of the population to be immunized against the protection of the herd. In the worst-case scenario, for example, if we do not move away physically or take other measures to delay the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus can infect this large number of people in a matter of months. It would overwhelm our hospitals and lead to high death rates.
At best, we maintain or even reduce current levels of infection until a vaccine is available. This will require a concerted effort by the whole population, with some level of continuous physical distancing for an extended period, probably a year or more, before a highly effective vaccine can be developed, tested and mass produced.
The most likely case is somewhere in between, where infection rates increase and decrease over time; we can relax social distancing measures when the number of infections decreases, and then we may need to implement these measures as the number increases again.
A prolonged effort will be required to prevent major epidemics until a vaccine is developed. Even then, SARS-CoV-2 could infect children before they can be vaccinated or adults after their immunity decreases. But it is unlikely in the long run that the explosive spread we are seeing now, as a large part of the population will be immunized in the future.
With some other diseases, such as chickenpox before the chickenpox vaccine was developed, people have sometimes been intentionally exposed as a means of achieving immunity. For less serious illnesses, this approach may be reasonable. But the SARS-CoV-2 situation is very different.
COVID-19 carries a much higher risk of serious illness and even death. The death rate for COVID-19 is unknown, but current data suggests that it is 10 times higher than for influenza. It is even higher among vulnerable groups such as the elderly and people with weakened immune systems.
Even if the same number of people end up infected with SARS-CoV-2, it is best to space them out over time to avoid overwhelming our doctors and hospitals. Faster is not always better, as we have seen in previous epidemics with high mortality rates, such as the 1918 influenza pandemic. Scientists are working hard to develop an effective vaccine. Meanwhile, since the majority of the population is not infected with SARS-CoV-2, some measures will be necessary to prevent explosive outbreaks.

More Stories
AIBE 19 Result: Bar Council of India to Announce Soon – Key Details for Candidates
CUET PG 2025 Admit Card: Key Details and Important Updates
Changes in CUET Subject Combinations: Impact on Science and Commerce Students